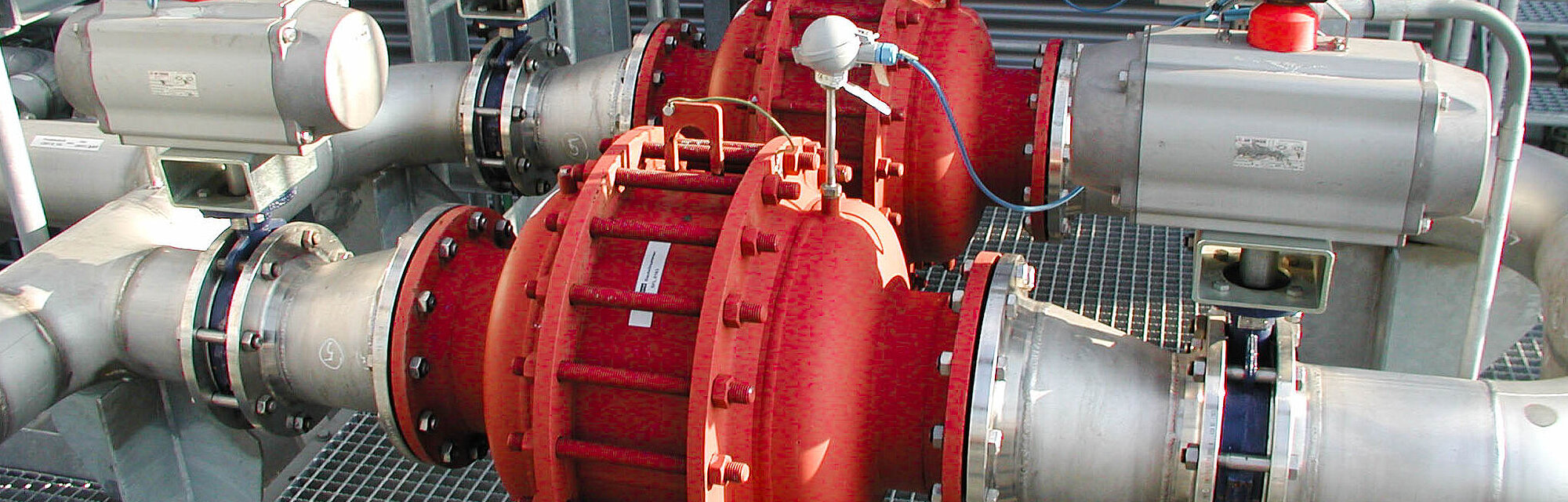
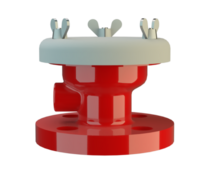
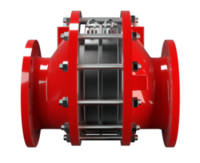
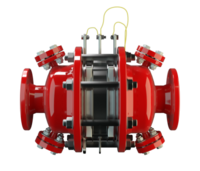
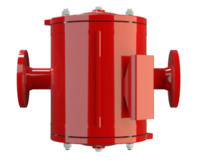
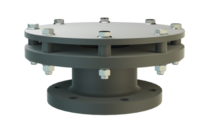
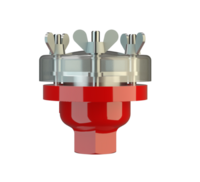
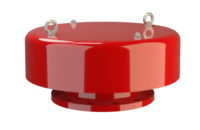
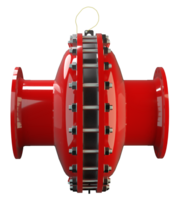
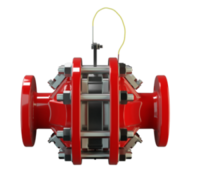
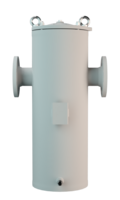
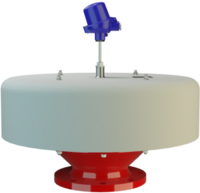
阻火器经过精心设计,允许气体和液体等流动,并可防止火焰传播。
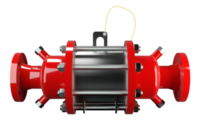
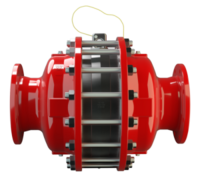
PROTEGO® 阻火器由单独的阻火盘 (FLAMEFILTER®)、间隔网和套管组成。阻火盘 (FLAMEFILTER®) 由卷绕的波纹金属条制成。PROTEGO® 管道末端阻火器和 PROTEGO® 管道中阻火器运用了狭小间隙中火焰淬熄的原理。
当混合物在两壁之间的间隙中着火时,火焰会朝未燃烧混合物蔓延。燃烧中混合物的体积膨胀会预压缩未燃烧混合物,并加速火焰的蔓延。通过边界层“s”中的散热,将热量传递到相对于间隙宽度“D”的间隙长度的较大表面上,然后通过将产品冷却至低于其着火温度,从而使火焰熄灭。
阻火器的间隙宽度和间隙长度决定了其灭火能力。间隙越窄越长,灭火效果越好。间隙越宽越短,压力损失越小。实验可以确定两种状况之间的最佳解决方案。
Explosion Group:
IIA1,
D / IIA,
C / IIB1,
C / IIB2,
C / IIB3
Explosion Group:
IIA1,
D / IIA,
C / IIB1,
C / IIB2,
C / IIB3
Explosion Group:
IIA1,
D / IIA,
C / IIB1,
C / IIB2,
C / IIB3

Explosion Group:
IIA1,
D / IIA,
C / IIB1,
C / IIB2,
C / IIB3

Explosion Group:
IIA1,
D / IIA,
C / IIB1,
C / IIB2,
C / IIB3
影片解釋了爆燃和爆炸的區別和特徵
不同的气体具有不同的火焰传播能力,并根据其危险等级划分为多个爆炸组。其相应的标准为 MESG(最大实验安全间隙),即在实验室中针对产品的火焰传播能力而测得的特征数。
MESG(或标准间隙宽度)是测试装置内部腔室两个部分之间最大间隙宽度,对于所有浓度的受试气体或空气中的蒸气,当内部气体混合物被引燃并处于规定条件下时,这一间隙将防止外部气体混合物通过 25 mm 的长间隙而被引燃。
MESG 是相应气体混合物的一种属性 [EN 1127-1]。注:EN 60079-20-1 规定了测试装置和方法。最具爆炸性的成分接近于气体/蒸气-空气混合物的化学计量混合物。
| 爆炸组 | 最大实验安全间隙 (mm) | NEC | 用于测试阻火器的参考介质 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IIA1* | ≥ 1,14 | 甲烷 | |
| IIA | > 0,90 | D | 丙烷 |
| IIB1 | ≥ 0,85 | C | 乙烯 |
| IIB2 | ≥ 0,75 | C | 乙烯 |
| IIB3 | ≥ 0,65 | C | 乙烯 |
| IIB | ≥ 0,5 | B | 氢气 |
| IIC | < 0,5 | B | 氢气 |
The table shows the categorization of substances into the respective explosion group according to their MESG (IEC 79-1, EN ISO 16852).